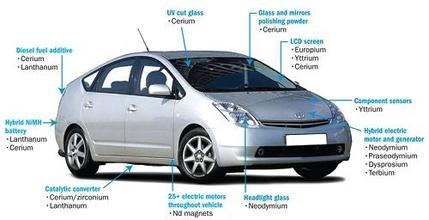
The Application of Rare Earth
Rare earth materials with special chemical and physical properties, so it has a wide range of applications in material, chemical, and nuclear energy, such as its main function is to improve the material performance and activity, it's main application:

1. Metallurgy: de-oxygen de-sulfur, and other injurious ingredients to act reducing agent, and making special alloys

2. Flint, ignition device

3. Catalyst for petroleum cracking process
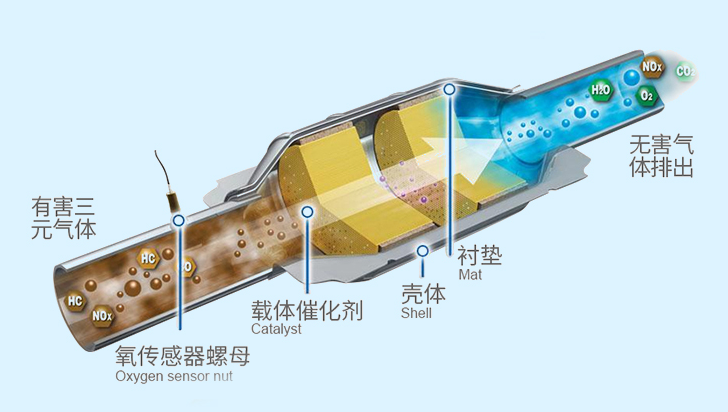
4. Purifying automobile exhaust gas

5. Glass precipitating and decoloring agents, glass and ceramic colorant

6. Permanent magnets SmCo, NdFeB
7. Super-conductor


8. Functional ceramic, yttria+zirconia, ceria+zirconia
9. Laser material, optical fiber optical lens, Lanthanum glass

10. Phosphor for color TV and lamp
11. Hydrogen storage, secondary battery

12. Polishing powder
13. Magnetic memory materials, Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging

14. Dye, leather industry: substitution of poisonous Cd pigments

15. Environmental protection: plastics degradation, paint and ink drier, Sewage treatment

16. Laser mater

17. Agriculture: foliar spraying and chemical fertilizer addition
18. Pharmaceutical industry, synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates

19. Artificial stones, Yttrium garnet

20. Electronic materials:Cr-Etchant

21. Rare earth doped target material
The main applications of each rare-earth element are as follows:
A table listing the seventeen rare earth elements, their atomic number and symbol, and their main usages (see also Technological applications) is provided here. Some of the rare earths are named after the scientists who discovered or elucidated their elemental properties, and some after their geographical discovery.
| Symbol | Name | Selected applications | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | Light aluminium-scandium alloy for aerospace components, additive in Mercury-vapor lamps.[4] |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | Yttrium-aluminium garnet (YAG) laser, yttrium vanadate (YVO4) as host for europium in TV red phosphor, YBCO high-temperature superconductors, yttrium iron garnet (YIG) microwavefilters.[4] |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | High refractive index glass, flint, hydrogen storage, battery-electrodes, camera lenses, fluid catalytic cracking catalyst for oil refineries |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | Chemical oxidizing agent, polishing powder, yellow colors in glass and ceramics, catalyst forself-cleaning ovens, fluid catalytic cracking catalyst for oil refineries, ferrocerium flints for lighters |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, core material for carbon arc lighting, colorant in glasses andenamels, additive in didymium glass used in welding goggles,[4] ferrocerium firesteel (flint) products. |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, violet colors in glass and ceramics, ceramic capacitors |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | Nuclear batteries |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | Rare-earth magnets, lasers, neutron capture, masers |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | Red and blue phosphors, lasers, mercury-vapor lamps, NMR relaxation agent |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | Rare-earth magnets, high refractive index glass or garnets, lasers, X-ray tubes, computer memories, neutron capture, MRI contrast agent, NMR relaxation agent |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | Green phosphors, lasers, fluorescent lamps |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | Rare-earth magnets, lasers |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | Lasers |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | Lasers, vanadium steel |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | Portable X-ray machines |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | Infrared lasers, chemical reducing agent |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | PET Scan detectors, high refractive index glass |